Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD)
- Home
- Metabolic Diseases
- Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD)
Urea cycle disorders (UCD) are a group of rare metabolic diseases that usually appear in infancy or early childhood. Leveraging our pioneering efforts in UCD research, Protheragen stands at the forefront of developing cutting-edge diagnostic tools to enhance the effective management of UCD. As your trusted partner in UCD diagnostic research, we provide unparalleled support to meet your research needs.
Urea cycle disorders (UCD) refer to a group of rare, hereditary metabolic diseases marked by the absence or deficiency of the enzymes or transporters which occur in the urea cycle. This cycle is considered one of the most important processes of metabolism whose general function is the excretion of ammonia, which is a harmful product of the protein metabolism, from the organism. Any activity that disrupts the urea cycle leads to an increase in ammonia in the bloodstream, resulting in hyperammonemia and possible severe neurological injury, coma, or death if not treated.
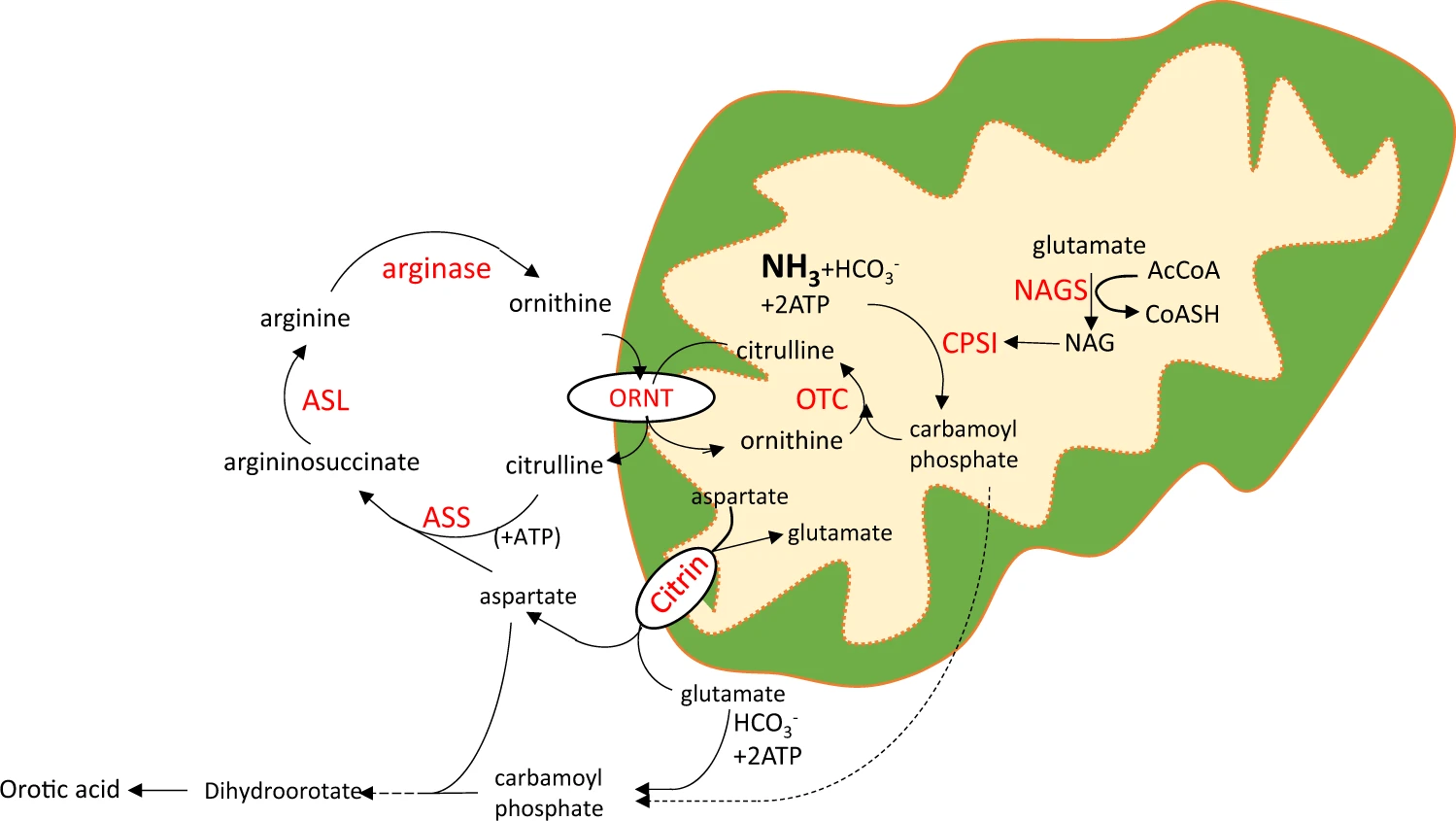 Fig. 1 A metabolic cascade of the urea cycle in the liver. (Matsumoto, Shirou, et al., 2019)
Fig. 1 A metabolic cascade of the urea cycle in the liver. (Matsumoto, Shirou, et al., 2019)
In diagnosing urea cycle disorders (UCD), the accurate identification of specific biomarkers is imperative as these reflect the metabolic derangemnts due to the insufficient functioning of the urea cycle. These biomarkers are measurable substances in the body that correspond to the metabolic disruptions and aid in distinguishing different types of disorders under the UCD group.
| Biomarkers | Description |
| Ammonia | Ammonia is a direct byproduct of impaired urea cycle function and is a critical biomarker for diagnosis and monitoring. |
| Amino Acid | Specific amino acids, such as glutamine and alanine, are often elevated in UCDs due to the body's attempt to detoxify excess ammonia. |
| Orotic Acid | Elevated levels of orotic acid in urine are a key biomarker for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD), the most common UCD. |
| Citrulline | Citrulline levels in blood or plasma can help differentiate between specific UCDs. |
| Argininosuccinic Acid | The presence of argininosuccinic acid in urine or blood is a specific biomarker for argininosuccinate lyase deficiency (ASLD). |
| Urea | Low levels of urea in the blood may indicate impaired urea cycle function, though this biomarker is less specific and often used in conjunction with other tests. |
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) tools are crucial for the timely and precise identification of urea cycle disorders (UCD). Defects in the urea cycle, are characterized by the toxic accumulation of ammonia in the blood which can lead to severe neurological damage and death if left unmonitored. The timely and precise detection of UCD facilitates better and more effective therapeutic measures. The development in the field of IVD aids health care practitioners to strive toward and provide better therapeutic outcomes with timely detection.

Current Status of IVD Development
Within the last few years, IVD tools development for UCDs has progressed significantly. Available diagnostic methods include the implementation of metabolite detection kits for ammonia, amino acids, and orotic acid, as well as genetic testing for mutations in urea cycle genes such as OTC, CPS1, and ASS1. There is wide utilization of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and next-generation sequencing (NGS) for precise and in-depth diagnostic testing.

Challenges of IVD Development
Nonetheless, the creation of IVD tools for UCDs encounters many obstacles, one of which is the intricate nature of biomarker signatures, which need advanced multiplexed assays for the precise quantification of ammonia, amino acids, and orotic acid. There is also an acute need for reliable point-of-care testing (POCT) to manage hyperammonemia crises. Meeting these challenges calls for new technologies, creative solutions, and partnerships aimed at producing dependable, practical, and affordable UCD IVD products.
Recognizing the challenges of urea cycle disorders (UCD) diagnosis, Protheragen is committed to the development of in vitro diagnostics (IVDs) for this rare metabolic disease to meet the unmet needs in this field. Our expertise lies in creating metabolite and genetic testing reagents/kits specifically for UCDs. These products, used in conjunction with supporting diagnostic devices, can achieve accurate and reliable testing to help timely diagnosis and intervention.

Additionally, Protheragen's services include point-of-care testing (POCT) and companion diagnostic development tailored for urea cycle disorders (UCD). These offerings are instrumental in facilitating rapid detection and personalized therapies of diseases. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more details and quotation information of related services.
Reference
All of our services and products are intended for preclinical research use only and cannot be used to diagnose, treat or manage patients.